The procurement project for Aramco
1.0 Executive Summary
The procurement project for Aramco is a comprehensive journey aimed at strategically optimizing the acquisition of goods and services. From its beginning as a back-office function under finance, procurement has become a pivotal department oversight within technology, managing a substantial budget for R&D labs. The department’s strategic role extends beyond cost management to actively drive innovation, sustainability, and risk mitigation. Aramco’s procurement function seeks to add long-term value through careful stakeholder analysis (TCO) considerations and a nuanced understanding of market dynamics. Recommendations for streamlining the procurement function encompass people development and process optimization. This endeavor positions Aramco to strategically align procurement functions with organizational goals, nurturing innovation while maintaining value creation.
2.0 Background
The Arabian American Oil Company (Aramco) is the national petroleum and natural gas company and one of the world’s largest and most valuable firms (Annual Report 2022, 2023). At Aramco, procurement began as purchasing, a back-office operation under the finance department’s control. As its significance grew, procurement became a tangible strategic function within technology oversight and coordination. The department is responsible for the expenditure of $ 110,000,000 for research and development Labs that produce tangible and intangible products, services and machines. The department works with researchers to discover new products that drive the growth and sustainability of Aramco while maintaining the bottom line and adding value in mitigating risks, saving money for the firm, and ensuring the firm obtains goods and services in a timely manner.

Source: Aramco
3.0 Introduction
Procurement refers to the comprehensive exchange process between two parties in the provision of materials or services at the appropriate time within the stipulated terms and conditions (Bag et al., 2020). It is essential to discern procurement from purchasing.
| Procurement | Purchasing |
| It is an umbrella term.Includes purchasing, identifying organizational needs, selecting suppliers, establishing payment terms, and managing supplier relationships. | It is a procurement function.Denotes how products are ordered. |
Table1: Differences between procurement and purchasing
Source: Author’s own
The Process spans the entire cycle from identifying needs to ending a services contract or until the end of an asset’s useful life.
Procurement involves options appraisal and the critical “make or buy” decision (Meyer et al., 2021). As such, it is a significant process that ensures all materials or services are appropriately acquired and correctly handled. According to Malacina et al. (2023), the Process has various business implications, including efficient material sourcing, cost optimization, timely materials and product delivery, and cash flow management.
In procurement, pricing arrangements can be divided into supplier and purchase pricing.
| Supplier pricing | Purchasers pricing |
| Mark upPremiumEconomySkimmingSpecial offers | Fixed target costsIncentivized gain shareIndexationPrice adjustmentCost reimbursableFixed prices with rebates |
Table 1: Purchasers vs Suppliers pricing
Source: Author’s own
The following chart shows the various costs accounted for by procurement.
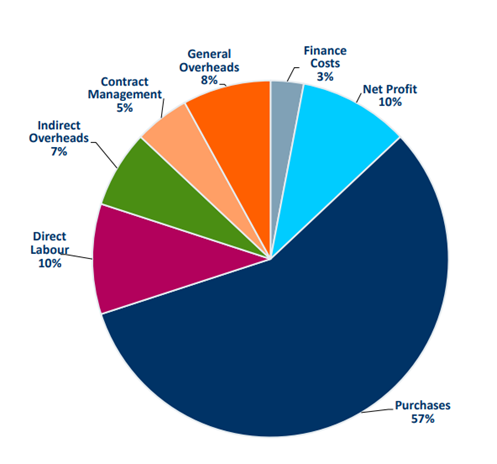
Source: Course material
Inala et al. (2023) suggest that for a fruitful procurement process, there is a need to have a list of potential sourcing, a robust relationship with suppliers and vendors, instituted policies, and an effective purchasing strategy. This paper delves into the intricacies of managing expenditures with suppliers by identifying a product, preparing a brief market analysis and demonstrating how the procurement function of purchasing will produce value-for-money outcomes.
Task One
4.1.1 Product
The identified product for this project is acetone. Acetone is among the most important chemical products in the research and development labs and is used as the primary solvent. It is a colorless liquid solvent that breaks down and dissolvse various substances. It is regarded as a safe chemical product with low toxicity and high flammability.
4.1.1 Importance
Acetone has various significances to Aramco. One of them is in chemical processing and synthesis. Owing to acetone’s versatility as a solvent, it is a critical component in various chemical reactions and processes involved in the production of petrochemicals. Another important role is in polymer production, whereby it is a key raw material. Aramco uses acetone in various processes that are related to polymer manufacturing. Acetone is also used to produce adhesives and coatings for numerous operations within Aramco. Another key usefulness of acetone to Aramco is as a solvent. Due to its strong solvent properties, acetone is used as a cleaning and decreasing substance in Aramco. This helps service equipment and ensures machinery operational efficiency.
4.1.2 Impact
Acetone has various implications for Aramco. One of them is operational efficiency. As a solvent and chemical processing agent, acetone contributes to the operational efficiency of Aramco. Its efficient use in various processes results in streamlined operations and decreased downtime. Another implication is in product quality. Consistent high-quality acetone contributes to the production of reliable and marketable products.
Acetone also has implications for cost management. The cost of acetone as a raw material impacts the overall cost structure of Aramco’s products. Efficient and cost-effective acetone procurement practices contribute to cost savings and enhanced financial performance for Aramco. Another implication is environmental and safety considerations. Using acetone, particularly in the oil and gas industry, poses various environmental and safety concerns. It is crucial to ensure compliance with environmental regulations and safety standards to avoid the destruction of the ecosystem and uphold worker safety.
4.1.3 Stakeholders
Mendelow’s power/ interest matrix below shows the stakeholders’ attributes regarding acetone.
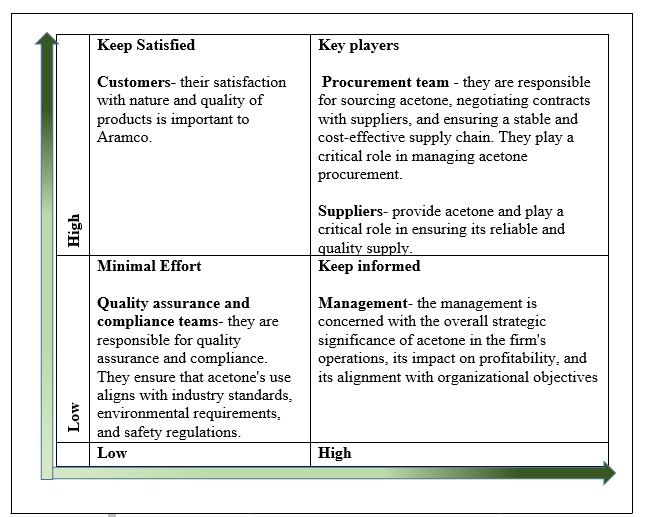
Table 2: Mendelow’s power/ interest matrix
Source: Author’s own
4.2 Task 2
4.2.1 Brief Market Analysis
The following section provides a brief market analysis for Aramco using Porter’s Five Forces. Porter’s Five Forces, published in 1979, is a tool marketing tool used to understand an industry’s attractiveness by investigating the five competitive forces of threat of new entrants, suppliers bargaining power, buyers’ bargaining power, threat from substitutes, and competitive rivalry between competing firms (Isabelle et al., 2020).
- Suppliers bargaining power
Suppliers have moderate bargaining power. According to Volza Grow Global, there are forty-two suppliers against ninety-seven buyers for acetone (Volza.LLC. (2020). Acetone suppliers have moderate bargaining power as they are in a higher concentration than buyers.
| Supplier | Revenue |
| Ineos | $85 billion |
| Shell | $108.54 billion |
| Formosa chemicals and Fiber corporation | $1billion |
Table 3: Key acetone suppliers
Source: Top Acetone Suppliers Based on Revenue | Beroe Inc. (2022)
- Buyers’ bargaining power
Buyers, such as Aramco, have moderate bargaining power. Although acetone is an essential input, the petrochemical industry mainly involves long-term contracts and relationships. With their large number and high purchasing power, companies such as Aramco have moderate power when negotiating favorable terms with suppliers.