Problem Set II Nucleic Acids: Replication, Transcription and Translation
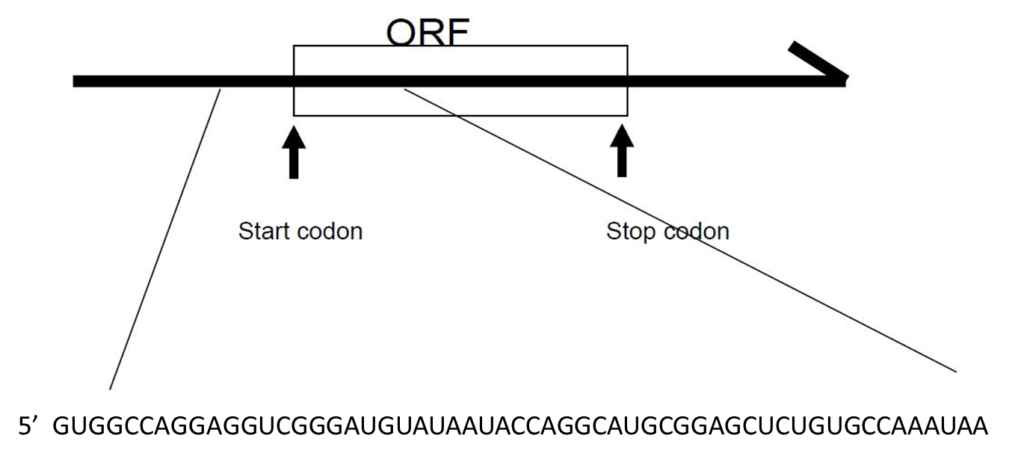
Problem 2. 7 points. Translate the mRNA open reading frame below. Write the amino acid primary sequence beginning with the START and ending with the STOP.
Problem 5. 5 points.
Below are two sequences of a segment of DNA.
Normal sequence TGA CAC TAG
Mutated sequence TGA CCT AG
Which type of mutation has occurred?
- Deletion
- Nonsense
- Insertion
- Substitution
Problem 6. 8 points.
Sickle cell anemia is caused by one amino acid substitution on the beta chain of hemoglobin. This hemoglobin is known as HbS.
Here is the DNA template sequences.
NORMAL 3’-TAC GGG AAA CAT TAG CTC AAA AAA…..-5’
MUTATED 3’-TAC GGG AAA CAT TAG CAC AAA AAA…..-5’
B. What is the peptide sequence translated from the normal gene?
C. What is the peptide sequence translated from the mutated gene?
D. Make a statement (complete sentences) regarding the amino acid change between the normal and the mutated gene for Hb. Based on what you know about the characteristics of the amino acids, how could this change affect the microenvironment of the peptide?
Problem 7. 5 points.
The genetic code is unambiguous. Although many amino acids have more than one codon (degenerate), each codon specifies only one amino acid (unambiguous). There is also the wobble theory which states that the anti-codon tRNA can recognize more than one codon due to the less-precise base pairs that can arise between the 3rd base of the codon and the base at the 1st position on the anticodon. Here are examples of codons.
| Valine | Leucine | Start |
| GUU | UUA | AUG |
| GUC | UUG | |
| GUA | CUU | |
| GUG | CUC | |
| CUA |
Given the above information which of the following statements most precisely describes the relationship between codons and amino acids. In your own words, state why you chose one answer and rejected the other four.
- The third base of the codon can wobble.
- The second base of the codon can wobble.
- The first base of the codon can wobble.
- The genetic code is unambiguous.
- The genetic code is degenerate.
Problem 10. 18 points.
- Draw a eukaryotic gene. Make sure it is double-stranded DNA.
- Number some of the bases upstream and downstream.
- Include and label the enhancer (distal) sequence.
- Include and label the proximal control elements: GC box and CAAT box.
- Include and label the TATA box.
- Label the START site.
- Include the Kozak consensus sequence.
- Label the CORE promoter.
- Label the 5’-Untranlsated region (UTR) and the 3’-Untranslated region.
- Include and label introns and exons.
- Include and label the polyA tail.
- Make sure you label whether the DNA sequences are on the coding sequence or the template sequence of the DNA.
Problem 11. 8 points.
In your own words, explain how the initiation complex for transcription is different between prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Use the essay style – introduction sentence(s), information sentences, conclusion/closing sentence(s).